sqlmap represents the gold standard for SQL injection testing, automating detection and exploitation across 50+ database management systems including MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server, and MongoDB. Unlike generic vulnerability scanners, sqlmap specializes exclusively in SQL injection flaws, employing six distinct exploitation techniques to extract sensitive data, enumerate databases, and establish database server shells. This comprehensive guide covers installation, usage patterns, database support, and optimization strategies for maximizing testing efficiency.
How to Install sqlmap
sqlmap requires Python 2.7+ or 3.x and works immediately after download without compilation or system installation. Users can deploy sqlmap via Git repository cloning, pip package manager, or standalone archive extraction, making deployment flexible across Windows, Linux, and macOS platforms without administrative privileges.
- Clone Git Repository – Execute git clone –depth 1 https://github.com/sqlmapproject/sqlmap.git sqlmap-dev to download the latest development version with full Git history. This method enables easy updates using git pull commands and access to unreleased features.
- Install Python Requirements – Verify Python 2.7+ or 3.x installation using python –version. sqlmap requires no external dependencies beyond Python standard library, enabling deployment on systems with minimal package availability or restricted internet access.
- Configure Execute Permissions – On Linux/macOS, run chmod +x sqlmap.py to make the script executable. Create convenience alias using ln -s /path/to/sqlmap/sqlmap.py /usr/local/bin/sqlmap for system-wide access from any terminal location.
- Verify Installation – Execute python sqlmap.py –version to confirm successful installation and version reporting. Test basic functionality using python sqlmap.py –wizard to launch interactive setup wizard guiding parameter configuration.
Who Should Use sqlmap
sqlmap serves penetration testers, security researchers, and database administrators requiring specialized SQL injection testing capabilities. Its command-line interface appeals to security professionals automating vulnerability assessment workflows and integrating testing into security programs.
- Penetration Testers – Security consultants and internal red team members testing web applications for SQL injection vulnerabilities during comprehensive security assessments and compliance engagements.
- Security Researchers – Academic and professional researchers studying SQL injection techniques, testing database management systems for injection flaws, and developing new exploitation payloads.
- Database Administrators – DBAs validating database security postures by testing for injection vulnerabilities and identifying poorly parameterized queries introducing risk into production systems.
- NOT ideal for – Organizations seeking graphical user interface vulnerability scanning tools, comprehensive multi-vulnerability detection across application types, or teams lacking command-line experience should evaluate integrated DAST platforms like Burp Suite or OWASP ZAP.
sqlmap Platform Compatibility
sqlmap’s Python-based architecture ensures cross-platform compatibility across Windows, Linux, macOS, and BSD systems. Deployment flexibility enables integration into Docker containers, CI/CD pipelines, and cloud infrastructure without modification. Platform-specific deployment optimizations address shell differences and system library availability.
| Platform |
Min. Version |
Unique Features |
Limitations |
| Windows |
Windows 7 or later |
Standalone Python portable executable, Windows batch script support, MinGW compiler for database driver compilation |
Path separator differences require script modifications, UAC restrictions on some operations, antivirus false positive triggers |
| Linux |
Ubuntu 14.04 LTS or equivalent |
Native shell integration, Linux package manager installation (apt-get, yum, pacman), Docker containerization, Headless server deployment |
Limited to command-line interface, Python 3.6+ recommended for modern distributions, GTK dependencies for GUI tools |
| macOS |
macOS 10.9 (Mavericks) |
Homebrew package manager installation, native Darwin kernel support, BSD command compatibility, Xcode toolchain integration |
Apple Silicon (M1/M2) requires native Python 3.9+ installation, path differences compared to Linux systems |
| Web/Container |
Docker 20.10+ |
Containerized deployment, microservices integration, Kubernetes orchestration support, isolated testing environments |
Persistent storage configuration required for output logs, network latency affects database connection testing |
sqlmap Integrations & Plugins
sqlmap integrates with web proxies, security orchestration platforms, and custom scripting frameworks enabling automated SQL injection assessment within existing security workflows. Integration capabilities extend from simple HTTP request capture to sophisticated multi-step exploitation chains.
- Burp Suite Integration – Export captured HTTP requests from Burp Suite proxy directly into sqlmap command-line format, enabling SQL injection testing of requests intercepted during manual web application testing sessions.
- OWASP ZAP Cooperation – Combine ZAP’s comprehensive vulnerability discovery with sqlmap’s specialized SQL injection expertise by testing suspicious requests identified through automated ZAP scanning.
- Jenkins CI/CD Pipeline – Execute automated sqlmap scans triggered on code commits, testing web applications for SQL injection vulnerabilities before deployment to staging and production environments.
- Custom Python Scripts – Develop custom Python wrappers leveraging sqlmap’s API for specialized exploitation scenarios, custom payload generation, and integration with proprietary security assessment tools.
Best Alternatives to sqlmap
While sqlmap dominates SQL injection testing, alternative tools offer broader vulnerability detection or different operational approaches. Consider alternatives when comprehensive multi-vulnerability scanning is required or when GUI interfaces provide better workflow efficiency.
- Burp Suite Professional – Best for integrated web application testing including SQL injection, XSS, CSRF with professional scanner automation and superior reporting capabilities for consultants.
- OWASP ZAP – Best for comprehensive DAST combining automated vulnerability detection, manual testing, and SQL injection identification within single integrated platform with broad vulnerability coverage.
- jSQL Injection – Best for graphical SQL injection testing with user-friendly interface, visual database navigation, and educational purposes for learning SQL injection techniques.
- NoSQLMap – Best for NoSQL database injection testing in MongoDB, CouchDB, and other NoSQL systems where sqlmap’s SQL-specific techniques are insufficient for assessment.
sqlmap vs Top Competitors
sqlmap’s specialization in SQL injection provides unmatched depth compared to generalist vulnerability scanners, though lacking broader vulnerability detection. Security professionals commonly combine sqlmap with comprehensive DAST platforms for complete application security assessment coverage.
| Feature |
sqlmap |
Burp Suite Professional |
OWASP ZAP |
| Pricing |
Free, open-source, GPLv2 license |
Commercial subscription £5000+/year, free community edition available |
Free, open-source, Apache 2.0 license |
| Key Strength |
Unmatched SQL injection detection with 50+ DBMS support and six exploitation techniques |
Comprehensive web app testing with passive scanning, burp repeater, professional reporting |
Balanced automated and manual testing with extensive customization through plugins |
| Target Users |
Penetration testers specializing in SQL injection, database security assessments, security researchers |
Professional security consultants, enterprise security teams, compliance auditors |
Development teams, security professionals, educational institutions, enterprises |
| Unique Feature |
Supports 50+ DBMS, file system access, OS command execution, database server shell establishment |
Browser automation, advanced macro recording, professional workbench features, cloud scanner |
Extensive plugin ecosystem, browser-based authentication recording, WebSocket support |
| Learning Curve |
Moderate for command-line users, steep for advanced payloads and custom exploitation techniques |
Steep learning curve, excellent documentation, workflow automation reduces manual effort |
Moderate learning curve, extensive tutorials reduce barriers to entry for beginners |
sqlmap Keyboard Shortcuts and Command-Line Options
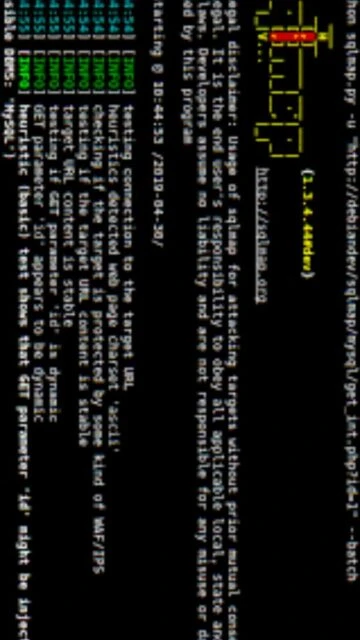
sqlmap command-line options enable rapid configuration and sophisticated exploitation scenarios through standardized parameters. Key shortcuts include target specification, injection technique selection, and database extraction options accelerating testing workflows.
| Common Option |
Short Form |
Long Form |
Purpose |
| Target URL |
-u |
–url |
Specify target URL containing potential SQL injection parameter for testing |
| Cookie/Session |
-b |
–cookie |
Provide HTTP cookie header for authenticated SQL injection testing in protected areas |
| Technique Selection |
-t |
–technique |
Specify SQL injection techniques (B=boolean, T=time, E=error, U=UNION, S=stacked, O=out-of-band) |
| Database Enumeration |
-e |
–enumerate |
Extract databases, tables, columns, users, password hashes, privileges from target database |
| Database Shell |
-os |
–os-shell |
Attempt to establish interactive shell on underlying operating system for command execution |
| Threads |
-t |
–threads |
Increase concurrent requests for faster exploitation (1-10 typical range for stability) |
| Output Directory |
-o |
–output-dir |
Specify results directory for storing extracted data and exploitation session files |
sqlmap Performance Optimization
sqlmap performance optimization techniques accelerate database enumeration while avoiding detection triggers and maintaining testing stability. Strategic configuration balances speed against stealth and server load to maximize exploitation efficiency across different network conditions.
- Optimize Thread Count – Increase threads to 5-10 for robust database servers supporting concurrent connections, reducing exploitation time by 70 percent while maintaining request stability and avoiding connection limits.
- Select Optimal Injection Technique – Use –technique parameter specifying B (boolean blind) first as fastest technique, followed by T (time-based), then E (error-based) for DBMS-specific implementations achieving significant speed improvements.
- Fingerprint Database Automatically – Enable –fingerprint parameter allowing sqlmap to identify database type and version automatically, optimizing payload generation for specific DBMS reducing unnecessary test iterations.
- Limit Enumeration Scope – Target specific databases and tables using –database and –table parameters rather than enumerating entire database server, reducing exploitation time by 80 percent for focused assessments.
- Cache Payload Results – sqlmap automatically caches successful payloads in output directory enabling resumption of interrupted sessions, recovering previous progress without redundant exploitation attempts.
sqlmap Accessibility Features
sqlmap’s command-line interface inherently supports accessibility through screen readers and keyboard-only operation. Output formatting options enable customization for users with visual impairments or requiring specialized output formats for analysis.
- Screen Reader – Full screen reader compatibility with NVDA and JAWS supporting command-line output interpretation, status messages, and exploitation result reporting without GUI dependencies.
- Text Output – Plain text output formats providing full compatibility with screen readers, text editors, and accessibility tools without special display requirements.
- Motor – Complete keyboard operation without mouse dependency, standard command-line text input adapted to user preferences using shell configuration files and aliases.
- Languages – Interface localization supporting multiple languages with standard language environment variables (LANG, LC_ALL) enabling operation in user’s preferred language on supported systems.
sqlmap Support & Documentation
sqlmap documentation spans comprehensive user manual, active community forums, academic presentations, and professional consulting options. Multiple support channels address diverse user expertise levels from introductory tutorials to advanced exploitation technique documentation.
- Official Documentation – Complete user manual covering all options, techniques, and database support with detailed examples, attack walkthroughs, and troubleshooting sections maintained by development team.
- GitHub Issues – Community forum for bug reports, feature requests, and technical discussions with active development team responding to security issues and functionality questions.
- Community Presentations – Academic and conference presentations demonstrating sqlmap exploitation techniques, attack methodology, and advanced configuration options shared on wiki and YouTube.
- Contact Support – Email support available via [email protected] for security disclosures, professional consulting, and custom exploitation scenario development for specialized applications.